Home » Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy

Dr Thng Yongxian
Hepatopancreatobiliary & General Surgeon
MBBS • MMed • MRCS (IRE) • FRCSED • FAMS
What is Colonoscopy?
A colonoscopy is a diagnostic procedure that visually examines the interior of the colon and rectum using a flexible, camera-equipped tube called a colonoscope. This procedure is important for detecting colon polyps, cancers, and other conditions, affecting the large intestine.
Colonoscopy is recommended as a routine screening tool for colorectal cancer starting at age 45 for people at average risk. It can also help diagnose symptoms such as unexplained changes in bowel habits, rectal bleeding, and abdominal pain. The procedure not only aids in diagnosis but can also be therapeutic, allowing for the removal of polyps and tissue sampling.
When Is a Colonoscopy Recommended?
A consultation with a colonoscopy specialist may be recommended for several key reasons, ranging from routine screening to investigating specific symptoms. The main indications include:
-
Routine Cancer Screening: For individuals at average risk, regular screening for colorectal cancer is typically advised starting from age 45-50. This may be recommended earlier for those with significant risk factors.
-
Investigation of Symptoms: A colonoscopy is crucial for investigating symptoms such as rectal bleeding, chronic constipation or diarrhoea, persistent abdominal pain or bloating, unexplained weight loss, and changes in bowel habits.
-
Further Evaluation: It is often required to determine the cause of iron-deficiency anaemia or to follow up on abnormalities found on other tests like a CT scan or a Faecal Immunochemical Test (FIT).
-
Surveillance: Patients with a personal or strong family history of colorectal cancer or polyps, or those with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) like Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, require periodic colonoscopies for surveillance.
Benefits of Colonoscopy
Preparing for a Colonoscopy

Dietary Restrictions
- In the days leading up to the procedure, you will be required to follow a special low-fibre diet. For at least 24 hours before your colonoscopy, you will need to consume only clear liquids. This includes water, clear broths, black coffee or tea (without milk), and clear juices like apple juice. Avoid red or purple-coloured drinks.

Bowel Preparation
-
To cleanse your colon completely, you must take a laxative preparation prescribed by your colonoscopy doctor. This may be a large volume of liquid that you drink over several hours or a smaller volume solution taken with other clear fluids. This preparation will induce diarrhoea to empty the colon, so it is important to stay at home and near a toilet during this time.

Medication Adjustments
-
It is crucial to discuss all medications, supplements, and health conditions with your doctor before your procedure. Some medications, particularly blood thinners (like aspirin, clopidogrel, or warfarin) and diabetes medications, may need to be adjusted or temporarily discontinued to ensure your safety during the procedure.
Enquire For Colonoscopy
Consult our dual fellowship-trained surgeon for a personalised treatment plan today.
Pre-Procedure Setup
Upon arrival at the clinic or hospital, you will be required to complete the necessary paperwork and change into a gown. You’ll then be taken to the procedure room.

Sedation
Most colonoscopies are performed under sedation to ensure comfort throughout the procedure. You will receive sedatives intravenously, which will make you feel drowsy.

Insertion of the Colonoscope
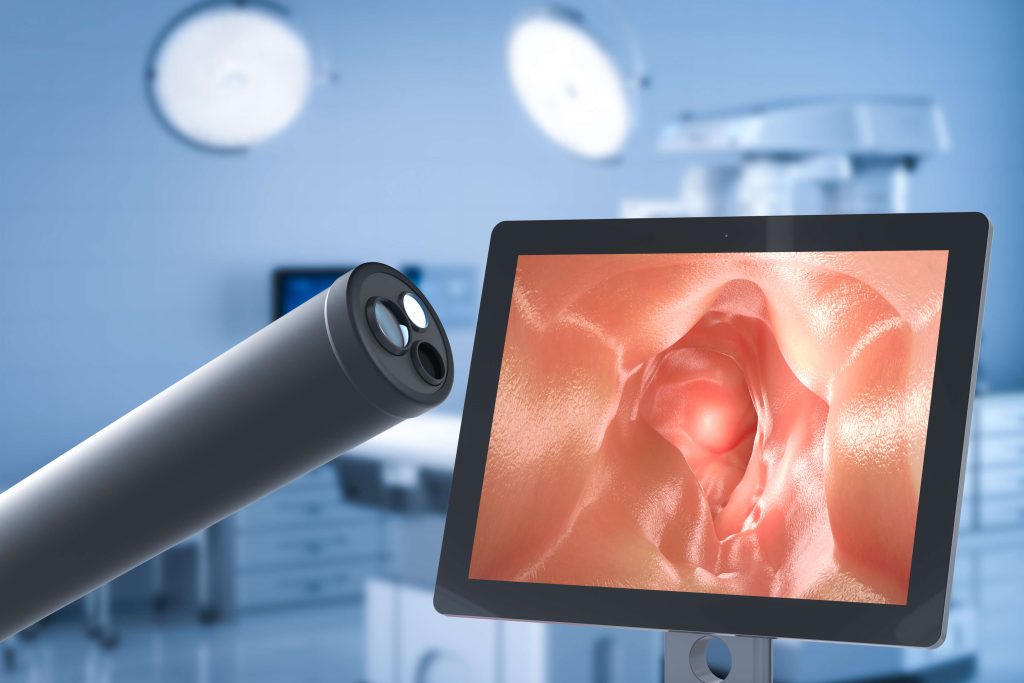
A long, flexible tube called a colonoscope will be inserted into the rectum and gently advanced through the colon. The colonoscope has a light and camera that sends images to a monitor, allowing it to examine the intestinal lining.

Examination and Intervention
As the colonoscope is manoeuvred through the colon, it is used to identify abnormalities like polyps or signs of inflammation. Tools can be passed through the colonoscope to remove polyps, take biopsies, or perform other necessary interventions.

Withdrawal and Inspection
The colonoscope is slowly withdrawn while the lining of the colon is inspected for any additional findings.
What Happens During Colonoscopy?
Understanding the procedure can help alleviate any anxiety. Our colonoscopy services are designed for patient comfort and safety.
-
Pre-Procedure Setup: Upon arrival at the clinic or hospital, you will complete the necessary paperwork and change into a medical gown. A nurse will review your medical history, and an intravenous (IV) line will be placed in your arm.
-
Sedation: To ensure you are comfortable and relaxed, most colonoscopies are performed under sedation. The sedative is administered through the IV, making you feel drowsy and relaxed. You will likely not remember the procedure afterward.
-
The Procedure: Once you are sedated, you will lie on your side, and your doctor will gently insert the colonoscope into your rectum. Air or carbon dioxide will be slowly introduced into the colon to inflate it slightly, allowing for a better view of the intestinal lining. The flexible colonoscope is carefully advanced through the entire length of the colon while images from the camera are transmitted to a monitor.
-
Examination and Intervention: As the colonoscope is withdrawn, the lining of the colon is meticulously inspected for any abnormalities. If polyps are found, they can usually be removed immediately using tiny tools passed through the scope. Tissue samples (biopsies) can also be taken for further analysis. The entire procedure typically lasts about 20 to 30 minutes.
Recovery and Aftercare Following Colonoscopy
It is important to follow specific aftercare instructions to ensure a smooth recovery after your colonoscopy. Here’s what you can generally expect:

-
Immediate Post-Procedure Care: After the colonoscopy, you will be taken to a recovery area, where nurses will monitor you as the effects of sedation wear off. This usually takes about 1 to 2 hours. You may feel mild cramping or bloating due to the air introduced into your colon; moving and walking can help relieve this discomfort.

- Observation for Complications: Although complications are rare, it’s important to monitor for any signs of trouble, such as severe abdominal pain, fever, bloody stool, or heavy bleeding from the rectum.

- Resuming Diet and Activities: You can usually eat and drink normally soon after the procedure unless advised otherwise. Most people can return to normal activities the following day.

- Managing Discomfort: You might experience mild cramping or bloating due to air introduced into the colon during the procedure. Walking and moving around can help dispel gas and alleviate discomfort.
-
Receiving Your Results: Your colonoscopy doctor will discuss the initial findings with you after the procedure. If biopsies were taken or polyps were removed, the results from the laboratory analysis will typically be available within a week.
Complications from a colonoscopy in Singapore are rare but possible. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe abdominal pain, a firm or bloated abdomen, persistent vomiting, fever, or significant rectal bleeding (more than a few tablespoons).

Dr Thng Yongxian
Senior Consultant
HEPATOPANCREATOBILIARY & GENERAL SURGEON
MBBS (SG) • MMed (Surg) • MRCS (Ire) • FRCSEd (Gen) • FAMS (Surg)
Dr Thng Yongxian is a dual fellowship-trained Hepatopancreatobiliary & General Surgeon who has performed over 6000 surgical procedures.
- Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery
- National University of Singapore
- Membership of the Royal College of Surgeons, Ireland
- Master of Medicine, General Surgery, Singapore
- Fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons, Edinburgh
- Fellow of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore
He pursued his subspecialty training in Hepatopancreatobiliary surgery first in the Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, Singapore General Hospital. Following this, he completed a clinical fellowship in Minimally Invasive Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery at Seoul National University Hospital in Bundang, South Korea.
Dr Thng set up and pioneered the Minimally invasive surgery program for his hospital in complex liver and pancreas cases. His surgeries were featured on live national television. His surgical videos have also been presented at international surgical conferences. He also pioneered the use of capsule colonoscopy for colorectal screening.
Dr Thng has served on various committees at hospital, cluster and ministry level. Dr Thng served as a member of the Ministry of Health (MOH) Laparoscopic cholecystectomy Clinician workgroup for value-driven care (VDC).
Frequently Asked Questions about Colonoscopy
Is colonoscopy painful?
Can colonoscopy detect all types of colon cancer?
A colonoscopy is the gold standard for detecting colon cancer and precancerous polyps, with very high accuracy. It allows for a direct visual inspection of the entire colon lining. While it is the most effective tool available, no medical procedure is 100% perfect, and there is a very small chance that tiny or flat polyps could be missed.
How long does it take to recover?
How often should I go for a colonoscopy?
What is the difference between FIT (Faecal Immunochemical Test) and Colonoscopy?
What is the difference between CT Colonography (Virtual Colonoscopy) and Colonoscopy?
Corporate and Personal Insurance Plans
Clinic Locations
Nexus Surgical @ Mt. Alvernia
- 820 Thomson Road #06-05, Singapore 574623
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturdays: 9.00am - 1.00pm
Sundays & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Mt. Elizabeth Orchard
- 3 Mount Elizabeth, #08-06, Singapore 228510
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturdays: 9.00am - 1.00pm
Sundays & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Mt. Elizabeth Novena
- 38 Irrawaddy Road, #08-43, Singapore 329563
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturdays: 9.00am - 1.00pm
Sundays & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Parkway East
- 319 Joo Chiat Place, #05-01, Singapore 427989
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturday, Sunday & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Gleneagles Medical Centre
- 6 Napier Road, #05-10, Singapore 258499
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturdays: 9.00am - 1.00pm
Sundays & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Mt. Alvernia
- 820 Thomson Road #06-05, Singapore 574623
- yongxian.thng@nexussurgical.sg
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturdays: 9.00am - 1.00pm
Sundays & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Mt. Elizabeth Orchard
- 3 Mount Elizabeth, #08-06, Singapore 228510
- yongxian.thng@nexussurgical.sg
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturdays: 9.00am - 1.00pm
Sundays & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Mt. Elizabeth Novena
- 38 Irrawaddy Road, #08-43, Singapore 329563
- yongxian.thng@nexussurgical.sg
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturdays: 9.00am - 1.00pm
Sundays & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Parkway East
- 319 Joo Chiat Place, #05-01, Singapore 427989
- yongxian.thng@nexussurgical.sg
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturday, Sunday & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Gleneagles Medical Centre
- 6 Napier Road, #05-10, Singapore 258499
- yongxian.thng@nexussurgical.sg
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturdays: 9.00am - 1.00pm
Sundays & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Mt. Alvernia
- 820 Thomson Road #06-05, Singapore 574623
- yongxian.thng@nexussurgical.sg
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturdays: 9.00am - 1.00pm
Sundays & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Mt. Elizabeth Orchard
- 3 Mount Elizabeth, #08-06, Singapore 228510
- yongxian.thng@nexussurgical.sg
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturdays: 9.00am - 1.00pm
Sundays & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Mt. Elizabeth Novena
- 38 Irrawaddy Road, #08-43, Singapore 329563
- yongxian.thng@nexussurgical.sg
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturdays: 9.00am - 1.00pm
Sundays & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Parkway East
- 319 Joo Chiat Place, #05-01, Singapore 427989
- yongxian.thng@nexussurgical.sg
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturday, Sunday & PH: Closed
Nexus Surgical @ Gleneagles Medical Centre
- 6 Napier Road, #05-10, Singapore 258499
- yongxian.thng@nexussurgical.sg
- (65) 9838 5827
- (65) 9838 5827
-
Mondays to Fridays: 9.00am - 5.00pm
(Lunch: 1:00pm - 2:00pm)
Saturdays: 9.00am - 1.00pm
Sundays & PH: Closed
Need help navigating your health?
Dr. Thng Yongxian extensive surgical experience includes specialised expertise as both a liver cancer surgeon and a gallbladder specialist. If you wish to learn more about our colonoscopy services or our other specialised treatments in Singapore, please contact our clinic today.